Elektromotor-Simulation für elektrische Maschinen und Antriebe
Entwerfen, analysieren und optimieren Sie Motoren und Generatoren direkt auf Basis Ihrer CAD-Modelle.
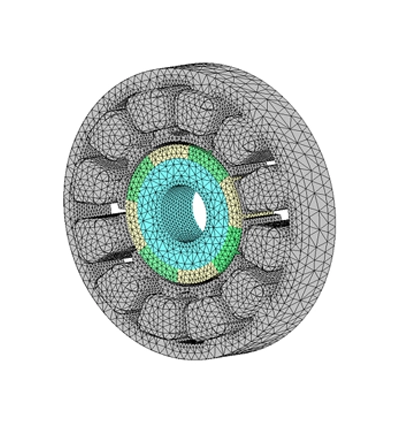
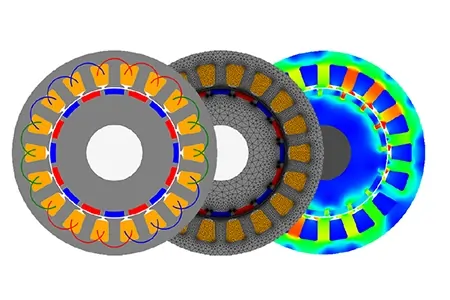
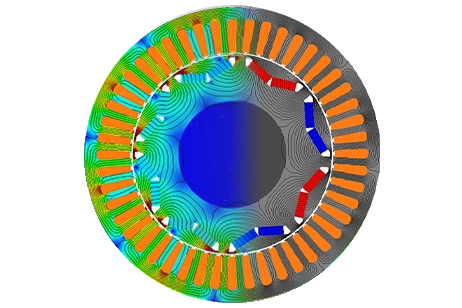
Ein BLDC-Motor wird mithilfe einer statischen Simulation mit EMS untersucht. Eine elektrothermische Analyse wird durchgeführt, um die Temperatur in der Wicklung zu berechnen.
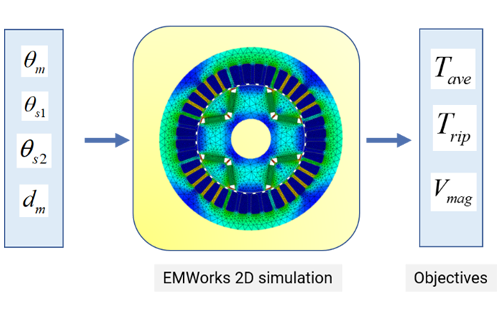
This application note analyzes a 12-slot/10-pole Halbach array permanent magnet motor using EMWorks. It compares three magnet ratios (Rmp = 1, 0.8, 0.5) in terms of cogging torque, back EMF waveform quality, electromagnetic torque, and torque density, showing how Halbach optimization affects motor performance for the same PM volume.
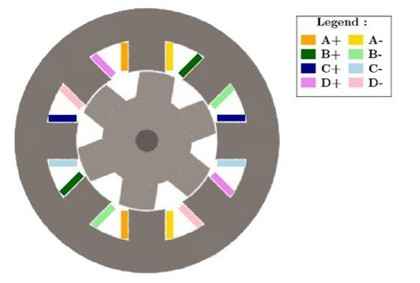
Ein Vierphasen-Schrittmotor mit einem Zahnrotor wird mittels magnetischer Wechselstromanalyse unter Verwendung von EMS analysiert."
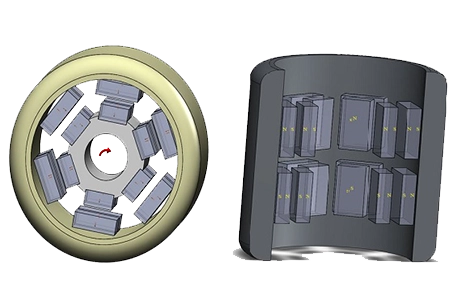
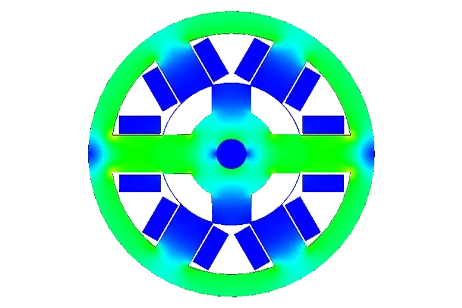
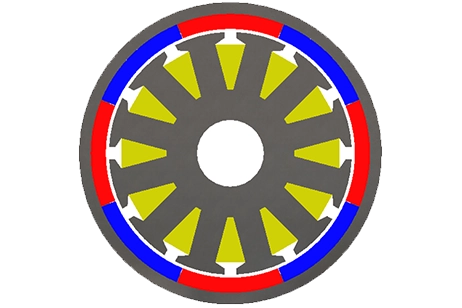
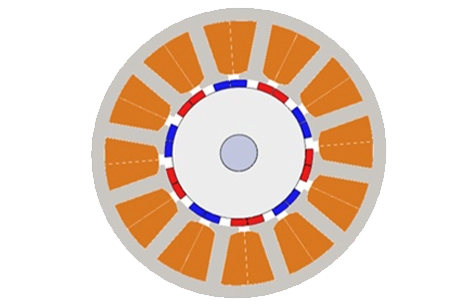
Permanentmagnetanordnungen in Form eines Stahlrotors mit 12 Permanentmagneten und eines Stahlstators mit weiteren 12 Permanentmagneten. Die Magnete sind abwechselnd radial nach innen und außen von der Zylinderachse polarisiert."
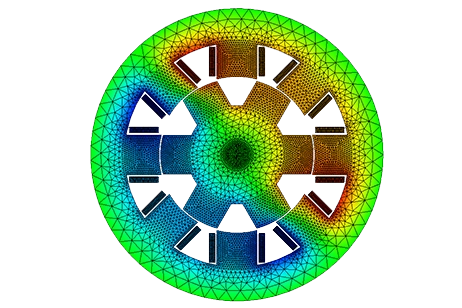
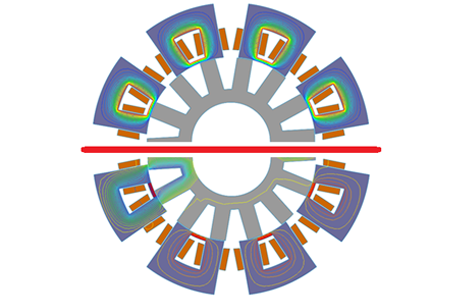
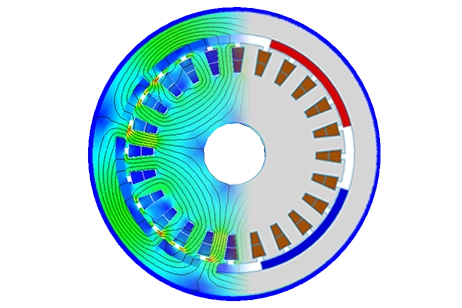
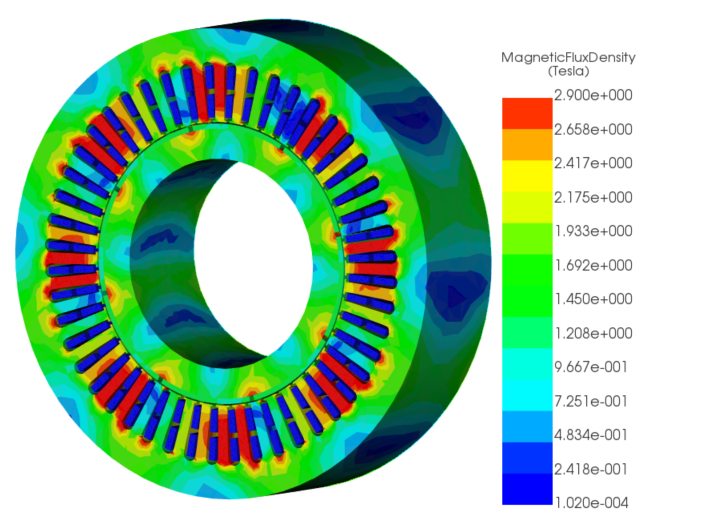
3D-Simulation eines geschalteten Reluktanzmotors (SRM) mit EMS for Solidworks.Computing und Visualisierung der magnetischen Flussdichte.
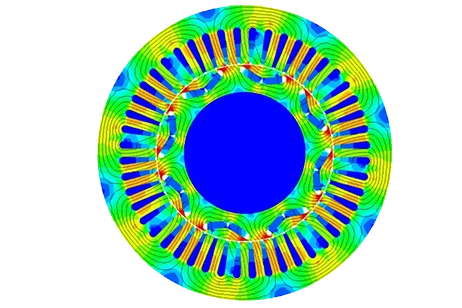
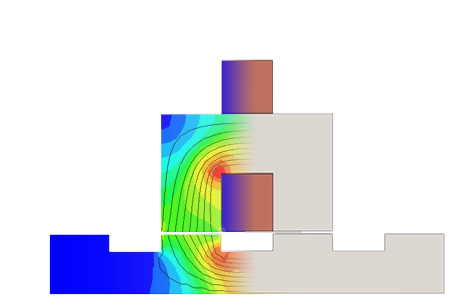
Ein geschalteter Reluktanzmotor (SRM) ist eine rotierende elektrische Maschine, bei der sowohl der Stator als auch der Rotor ausgeprägte Pole aufweisen (Abbildung 1). Die Statorwicklung umfasst einen Satz von Spulen, von denen jede auf einen Pol gewickelt ist.
This application note uses EMWorks to model a 3-phase, 12-slot/6-pole BLDC motor using 2D FEM. It reports torque, flux, inductance, and flux linkage versus rotor position to support early design decisions.
This note uses EMWorks MotorWizard to study how airgap length and rotor skew angle affect torque, efficiency, cogging torque, and torque ripple in a 24-slot, 8-pole inset PMSM, including a rare-earth-free design.
This note shows how EMWorks is used to model the Toyota Prius 48-slot, 8-pole IPM motor, compute torque, torque ripple, flux linkage, inductances and field plots, and use virtual prototyping to refine PMSM performance before hardware.
This application note compares a 4-phase 16/14 segmented SRM with a segmented-stator PM-assisted SRM using EMWorks2D transient magnetic analysis. By inserting permanent magnets in the slot openings, the PM-assisted topology increases average torque, power density, and efficiency while reducing torque ripple and iron usage, making it a compelling option for high-performance, cost-sensitive electric drive applications.
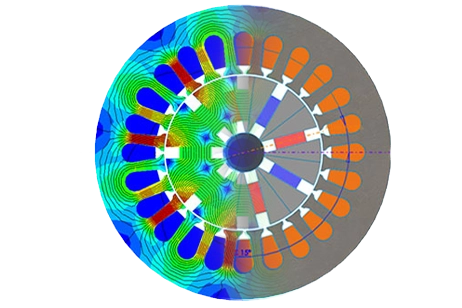
This application note uses EMWorks to study eccentricity faults in a Nissan Leaf interior PMSM. Static, dynamic, and mixed eccentricity are parameterized to evaluate their impact on air-gap flux, radial forces, torque, and torque ripple under load. The results show how eccentricity changes flux density, redistributes radial forces around the stator teeth, and can simultaneously increase average torque while reducing torque ripple, providing a practical framework for fault analysis and diagnostics in EV traction motors.
Finite element results for a 12-slot, 8-pole external rotor PMSM with magnet pole arc reduced from full pitch to 31°. A 31° arc yields the lowest cogging torque and much lower torque ripple with nearly unchanged average torque.
The note applies VDSE and surrogate models to an asymmetric IPMSM to lower torque ripple, maintain average torque, and reduce magnet volume.
Parametric study of two PMSM designs for aircraft use, showing how pole arc and back yoke dimensions affect torque ripple and total machine mass.
Comparison of symmetric and asymmetric IPMSM showing large reductions in cogging torque and torque ripple, with a slight increase in average torque and reduced magnet volume.
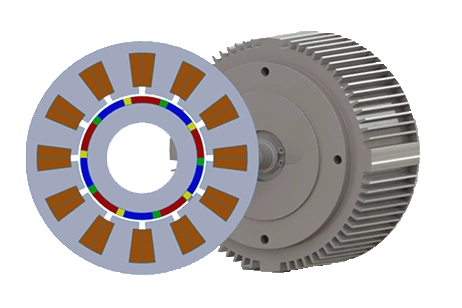
Gain valuable insights into the design and behavior of the 2004 Prius electric motor through detailed analysis and simulations. Explore its specifications, torque generation, and magnetic field distribution.
This page presents a 2D finite element study of cogging torque in a surface-mounted PMSM using EMWorks. The analysis computes and validates no-load cogging torque, then investigates how segmenting the permanent magnets into one, two, and three pieces per pole affects peak-to-peak torque. The results support design decisions for low-ripple traction and drive motors.
Linear switched reluctance motors are analyzed with 2D and 3D finite element models to compute magnetic flux density, inductance, and reluctance force versus translator position. The study compares longitudinal and transverse configurations, quantifying force density and inductance variation for different currents and alignments.
This application note evaluates a 6/4 switched reluctance motor using finite element analysis to quantify its static torque–angle and torque–current characteristics. The motor employs M-19 non-oriented silicon steel for both stator and rotor cores, with four phases and 120-turn copper coils per phase. A parametric sweep rotates the rotor from 0° (unaligned) to 46° (aligned) while monitoring magnetic flux distribution and electromagnetic torque for different phase currents. Results show that torque is essentially zero at the unaligned and fully aligned positions, with a maximum of roughly 0.30 Nm at about 18°, where the flux paths between stator and rotor poles are strongly coupled. Additional curves for multiple current levels confirm the expected proportional dependence of reluctance torque on phase current.
This application note uses 2D finite element analysis to evaluate a 24-slot/8-pole spoke-type permanent magnet motor. It reports cogging torque, no-load and on-load torque, flux linkage, induced voltage, and core loss for the selected materials and winding configuration.
This application note uses EMWorks2D to evaluate a 24-slot, 4-pole outer-runner PMBLDC motor in motor and generator modes, examining back EMF, torque, flux linkage, cogging torque, and core losses.
Key results for detent force, thrust, back EMF, losses and temperature in flat and tubular permanent magnet linear machines.
This application note models a 3-phase flat slotted iron-cored linear synchronous motor in EMWorks. It evaluates detent force, back EMF, thrust, flux density, and dynamic behaviour to quantify force ripple and support design choices for industrial linear drive applications.
This application note uses EMWorks to model an 8/6 switched reluctance motor and run static and on-load transient studies. The simulations compute field distribution, phase flux linkage, and torque versus time, providing practical insight into SRM behavior for design and control evaluation.
Finite-element analysis of stator inter-turn short circuits in a 8-pole PMSM, focusing on magnetic diagnostics and electromagnetic fault signatures.