Planar Printed Antenna Simulation with EMWorks
Design and tune PCB and integrated antennas for wireless and RF systems.
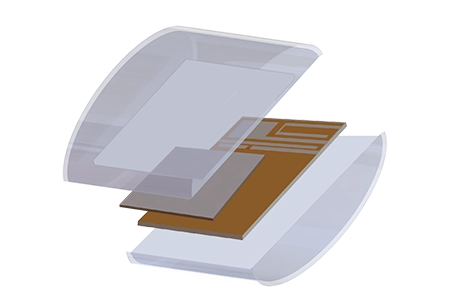
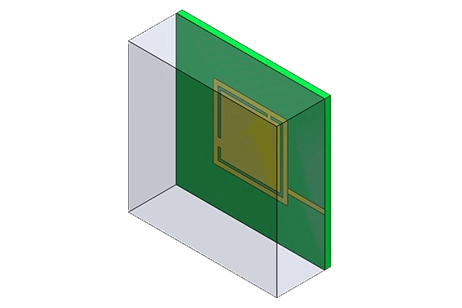
Design a compact printed inverted-F PCB antenna for IoT devices that operates over LoRa 915 MHz and GPS L1/L2 bands. This note shows how EMWorks simulations guide strip and slot tuning, account for casing and battery impact, and evaluate VSWR, efficiency, and radiation patterns.
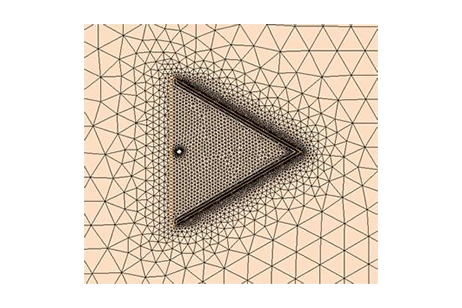
This note studies a single-feed microstrip antenna with spurs that creates dual resonances around 0.9 and 1.8 GHz for GSM bands. Fast-sweep antenna analysis and symmetry are used to match measured return-loss curves and validate the design.
This application note shows how EMWorks is used to design and optimize 5G mmWave antenna arrays. Starting from a single patch and scaling to 8×8 and 8×32 arrays, it highlights return loss, gain, and far-field metrics needed for high-gain 5G base-station antennas.
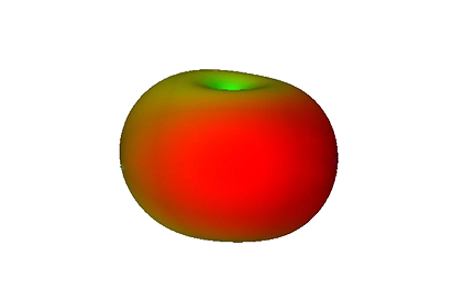
This note models a 2.4 GHz printed dipole antenna with an integrated BALUN and tapered feed in the RF & Microwave module, computing radiation patterns, gain and reflection coefficient over 1.8–3.8 GHz.
This application note presents the design of a compact 60 GHz patch antenna array with parasitic elements tailored for integration into Google Glass. The study compares configurations with and without parasitic elements, showing improved radiation patterns and elimination of nulls around 60° when parasitics are used. It also analyzes how mounting the antenna on Google Glass shifts the resonant frequency while preserving robust radiation performance, thanks to a full ground plane that isolates the antenna from the frame. The result is a wearable antenna solution that delivers reliable wireless connectivity in realistic smart-glasses environments.
This application note shows how to simulate a 2.45 GHz RFID tag antenna in EMWorks, from material setup and frequency sweep to return loss and radiation pattern evaluation. It helps you verify matching and field distribution before prototyping.
This application note studies a dual-band mm-wave patch antenna for 5G, using a square patch with L-shaped slots on RT/Duroid to realize resonances near 28 GHz and 38 GHz. The model includes a microstrip feed and parametric geometry, with S-parameters and far-field gain patterns extracted and compared to published measurements, demonstrating close agreement at 27.375 GHz and 37.125 GHz
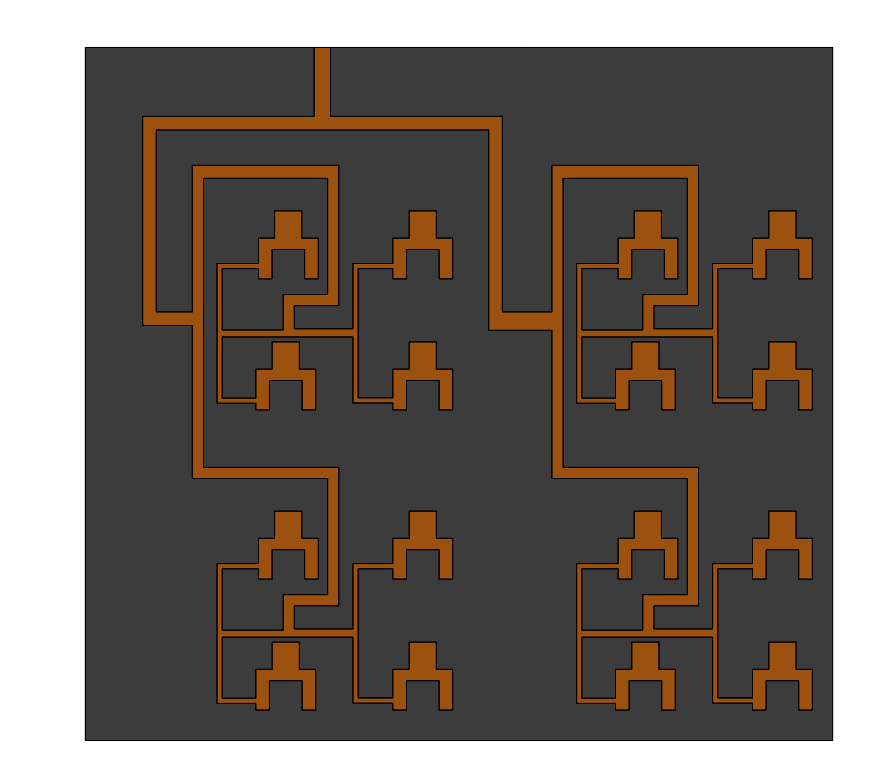
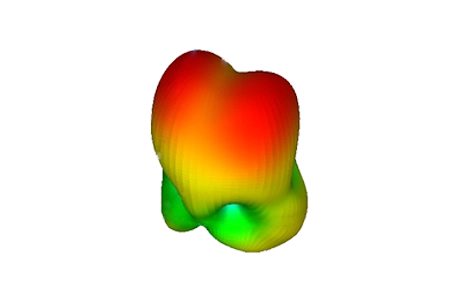
This example models a dual-band PIFA on a finite ground plane for GPS and WiMAX operation. The antenna combines driven and parasitic elements and is fully parameterized so you can study how geometric changes, such as strip length L3, affect S-parameters, bandwidth, and gain. Frequency-domain results include return loss and 2D/3D gain patterns at both resonances.
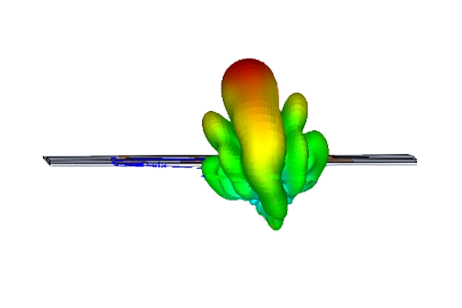
This example uses the RF & Microwave Antenna analysis to design and simulate a 2.45 GHz Bluetooth antenna for smartwatches in flat and bent configurations. By sweeping frequency and bending angle, it evaluates S11, VSWR, and far-field gain patterns to understand how mechanical deformation impacts resonance and link performance in wearable devices.
Rectangular dielectric resonator antennas (DRAs) are evaluated for 5G operation between 13 and 17 GHz. The study analyzes fundamental and higher-order modes in terms of S11 bandwidth, gain, dielectric losses and steady-state temperature. Simulated results are compared with published measurements to validate the DRA designs for 5G applications.
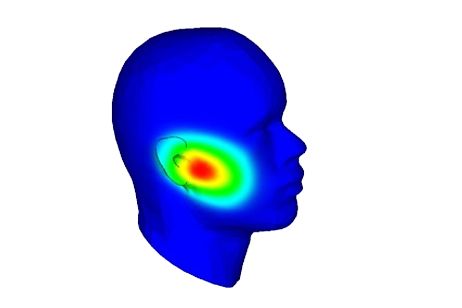
This note analyzes a printed GSM/LTE/WLAN phone antenna in free space and near a human head phantom. It reports return loss, radiation patterns, SAR, and temperature rise at 900 MHz and 2.45 GHz, and compares the results with common RF exposure limits.
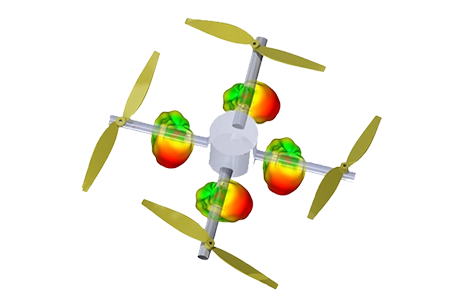
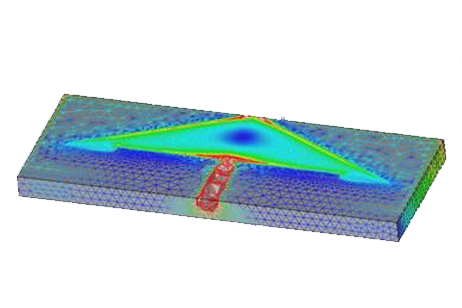
RF performance of a conformal 5.8 GHz drone antenna, covering return loss, gain, patterns, and coupling when installed on a multi-rotor UAV.
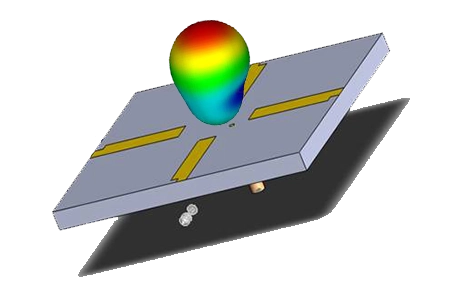
Design and analyze a 2×2 cm microstrip GPS patch antenna at 1.575 GHz in EMWorks, with detailed return loss and radiation pattern evaluation for portable GPS devices.
Simulate a printed circular monopole antenna in RF & Microwave. Evaluate S11, bandwidth, and radiation patterns using fast sweep and symmetry planes to reduce mesh size and solve time.


.webp)