Introduction
Inductance is an important parameter in DC solenoid and electromagnetic actuator design. It determines magnetic energy storage, influences current rise time, and reflects how effectively the magnetic circuit guides flux. Because inductance depends directly on the nonlinear B–H curve of the material, it serves as a practical measure of magnetic performance under DC excitation.
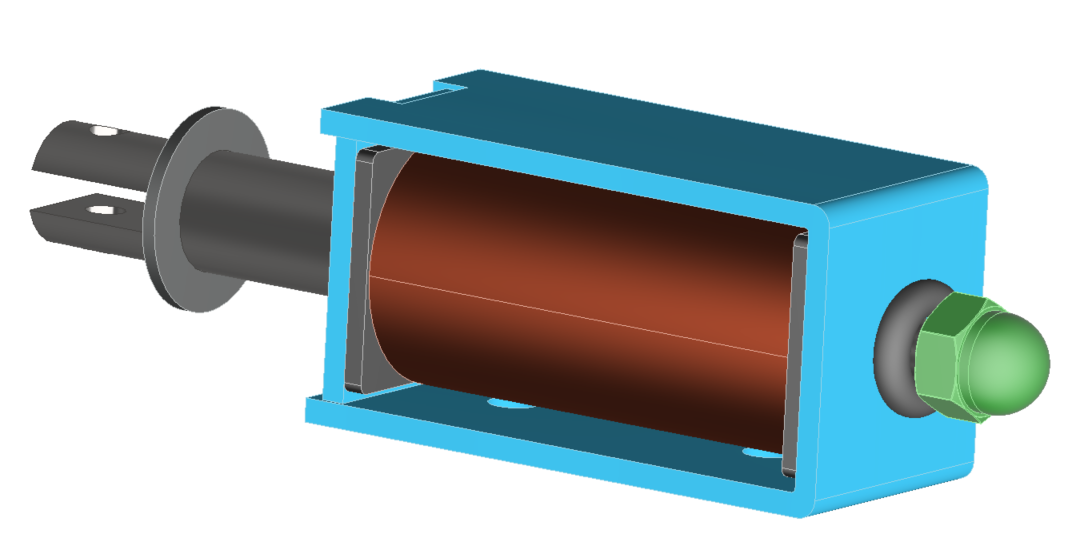
This application note compares inductance for six different materials assigned to the core, housing, and plunger of a DC solenoid. All simulations were performed using identical geometry and excitation to isolate the effect of material properties.
Model Setup
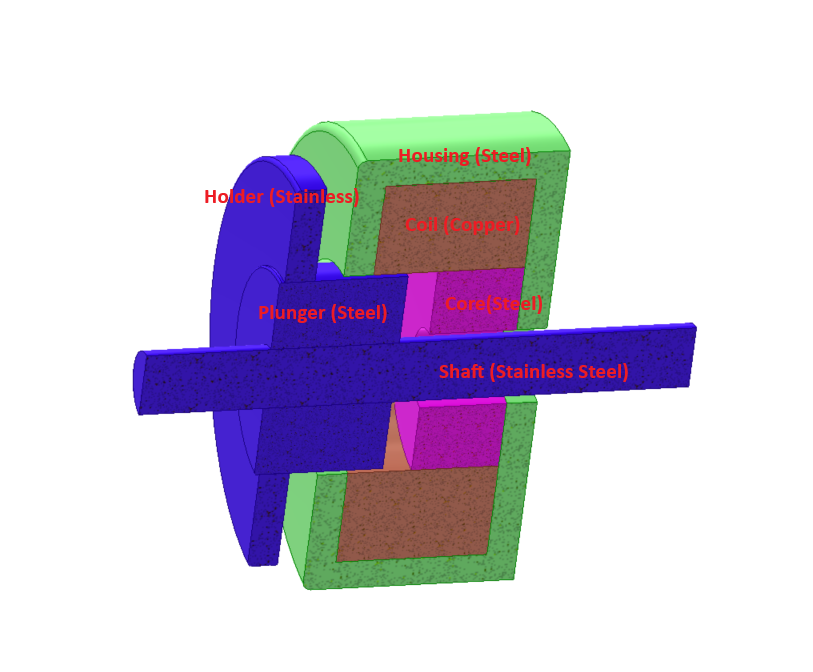
The model consists of a copper coil, a steel core, a steel housing, and a steel plunger. The shaft and front holder are stainless steel and remain non-magnetic in all cases.
Coil parameters:
- DC voltage: 33 V
- Turns: 432
- Wire: AWG 23 copper
- Steady-state current: I = 9.202 A
- Magnetomotive force: NI = 432 × I
Only the magnetic material used for the core, housing, and plunger varies across simulations.
Magnetic Materials Evaluated
Six materials were tested:
- AISI 12L14
- AISI 1010
- 20PNF1500 electrical steel made by POSCO
- M310-50A electrical steel made by Cogent
- Fluxtrol 25 made by Fluxtrol
- KoolMu 33µ powder material made by Magnetics
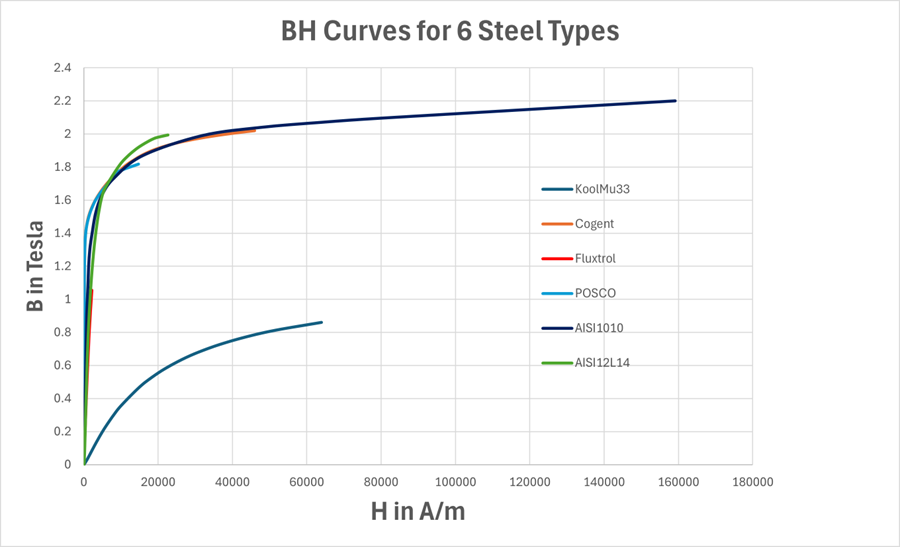
These materials represent a range of initial permeabilities and saturation levels, from high-performance electrical steels to soft magnetic composites.
Simulation Procedure
Inductance was computed using steady-state magnetostatic analysis in EMWORKS EMAG. All geometrical, meshing, and boundary conditions were identical between runs. The inductance was calculated from magnetic energy:
L = 2W / I2
where W is stored magnetic energy and I is the coil current.
Inductance Results
The computed inductance values are:
- AISI 12L14 — 0.0345 H
- AISI 1010 — 0.0391 H
- 20PNF1500 — 0.0434 H
- M310-50A — 0.0439 H
- Fluxtrol 25 — 0.0107 H
- KoolMu 33µ — 0.0114 H
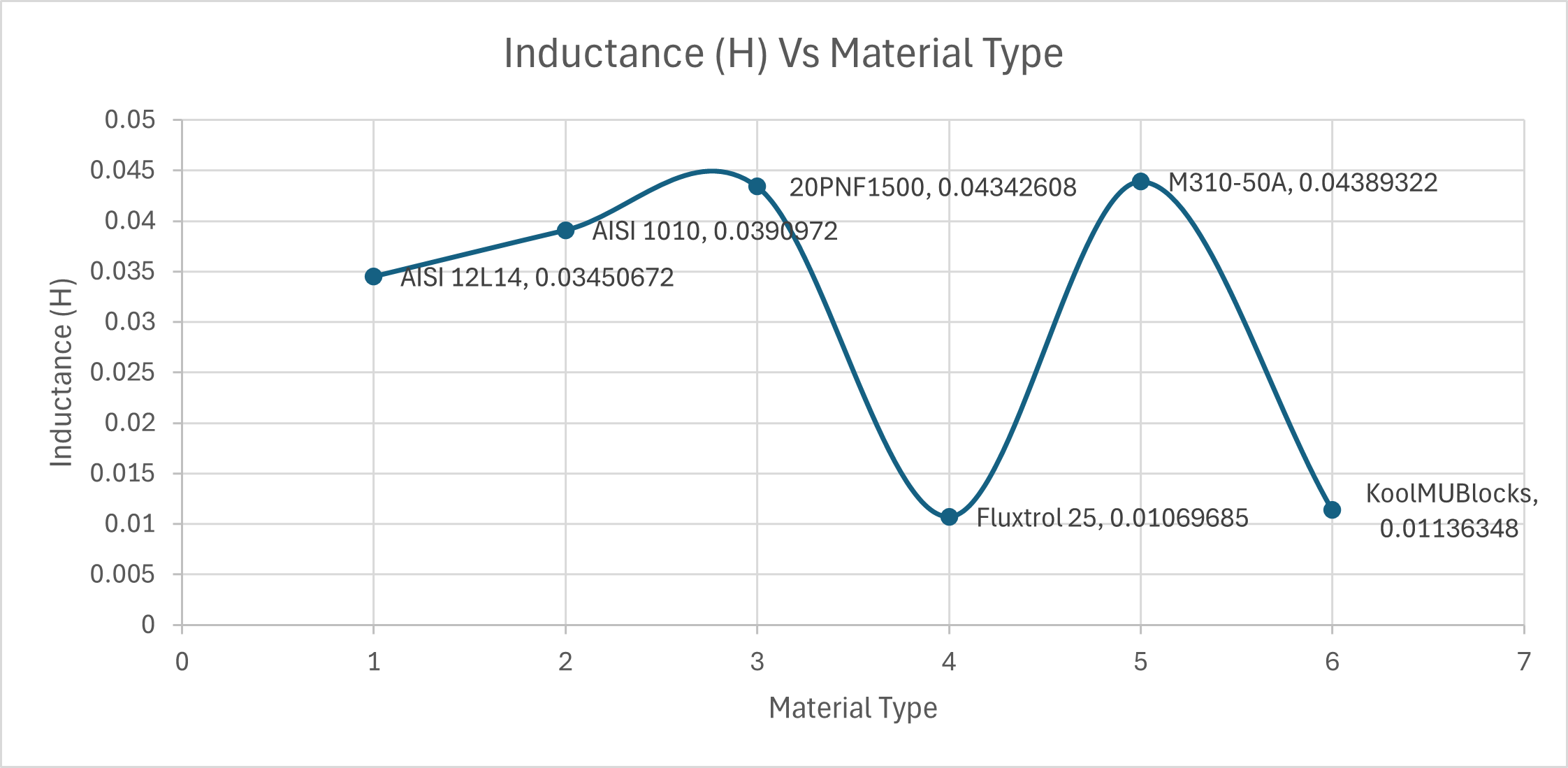
Electrical steels (20PNF1500 and M310-50A) exhibit the highest inductance due to their high permeability and high saturation flux density. AISI 1010 provides moderate inductance, while AISI 12L14 shows reduced performance consistent with its lower permeability. Fluxtrol 25 and KoolMu 33µ have low inductance because their DC permeability is significantly lower than that of steel.
Discussion
Inductance increases with effective permeability. Materials that can support high flux density with minimal saturation produce higher inductance. Electrical steels provide the largest increase, followed by low-carbon steels. Free-machining steel and soft magnetic composites produce significantly lower inductance. The inductance ranking matches the previously computed force ranking, confirming that material permeability governs both magnetic energy storage and actuator performance under DC excitation.
Conclusion
Material choice has a strong effect on solenoid inductance. Electrical steels provide the best performance, low-carbon steel offers a good balance of cost and magnetic response, and free-machining steels or composites should be avoided in DC applications requiring high inductance or strong magnetic force.
All simulations were performed using EMWORKS– EMAG, with identical excitation and geometry. The results illustrate how differences in B–H behavior directly influence inductance and DC solenoid performance.