Simulation linearer und rotatorischer Aktuatoren mit EMWorks
Entwurf, Dimensionierung und Optimierung elektromagnetischer Aktuatoren direkt auf Ihren 3D-Modellen.
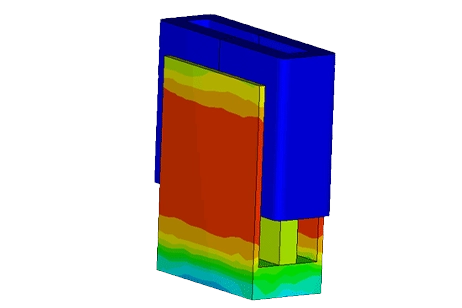
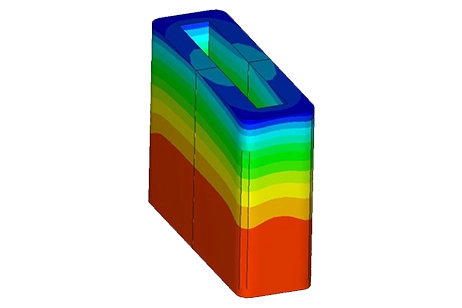
This application note explains how electro-thermal coupling affects voltage-driven solenoids. It shows how temperature-dependent copper resistance reduces current, magnetic flux density, and plunger force at steady state.
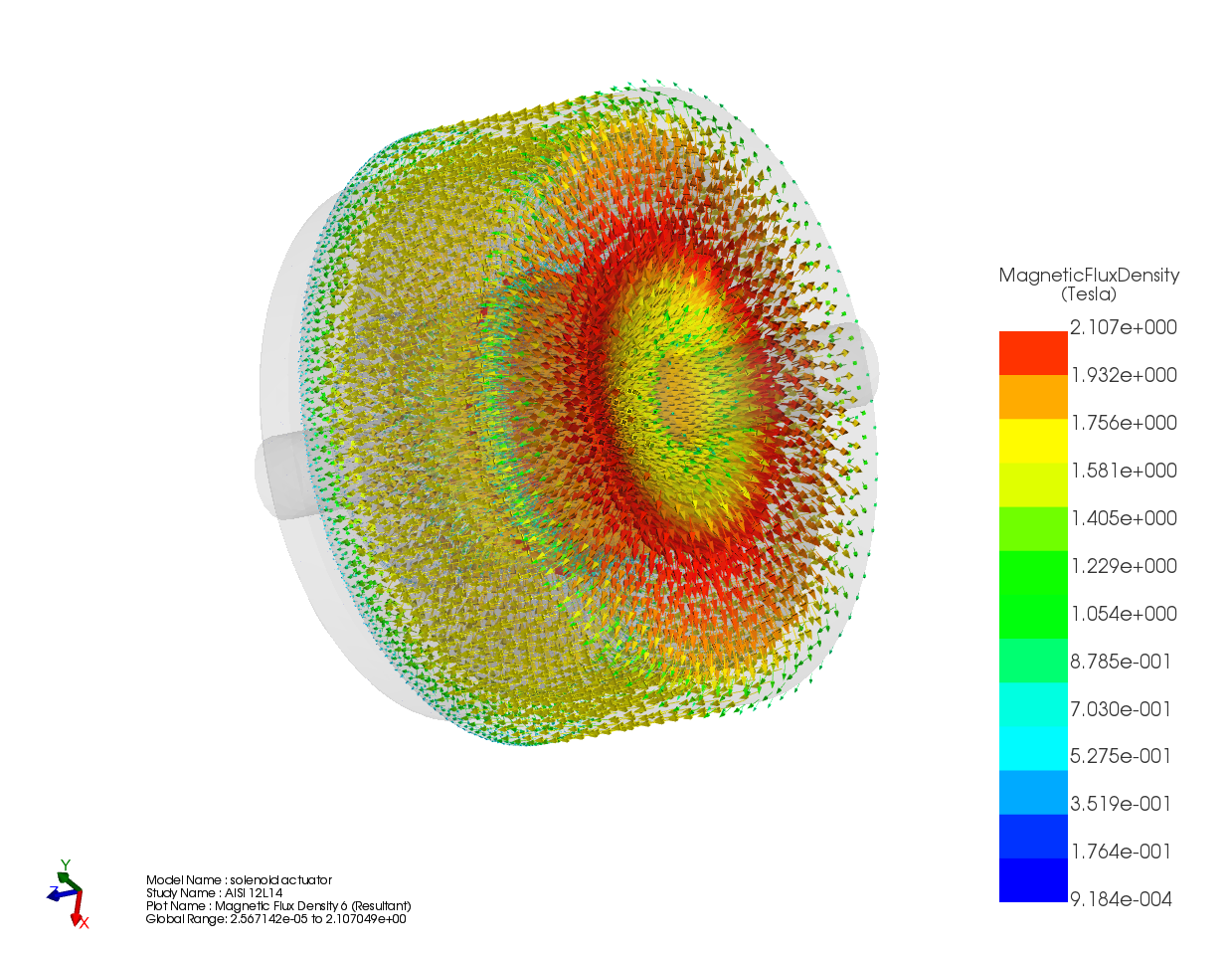
This application note uses EMWorks EMAG to study how different magnetic materials influence DC solenoid plunger force. For a fixed geometry and excitation, the force is computed for AISI 12L14, AISI 1010, electrical steels M310-50A and 20PNF1500, and soft magnetic composites Fluxtrol 25 and KoolMu 33µ. The results help engineers choose suitable materials for solenoid and actuator design.
This application note uses EMWorks EMAG to compare DC solenoid inductance for six magnetic materials, showing how B–H behavior and permeability affect actuator performance.
This application note examines how coil turns and wire gauge affect DC solenoid performance when the copper filling factor and AISI 1010 magnetic circuit are kept constant. Using EMWorks EMAG, three coils based on AWG 30, 23, and 20 are compared in terms of plunger force, copper loss, inductance, magnetic energy, and current density
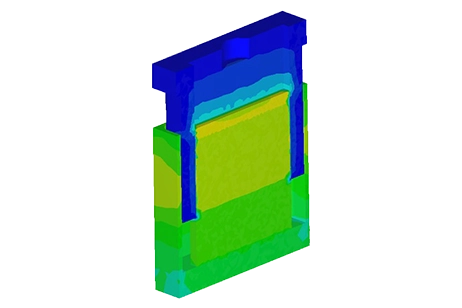
Eine magnetostatische Untersuchung eines mit "Motion" gekoppelten Solenoids. Die Studie untersucht die Auswirkung der durch den Strom induzierten elektromagnetischen Kraft auf den Kolben. Die Studie untersucht auch das thermische Verhalten der Struktur."
Das magnetostatische Modul von EMS in Verbindung mit SolidWorks Motion wird verwendet, um magnetische Ergebnisse (Fluss, Kraft usw.) und mechanische Ergebnisse (Verschiebung, Geschwindigkeit usw.) zu berechnen und zu visualisieren."
TEAM 24: Nichtlinearer zeitlich transienter Rotationsprüfstand
Magnetische Aktuatoren wandeln mithilfe elektromagnetischer Felder elektrische Energie in mechanische Energie um. In Abhängigkeit von der Bewegung, ob es sich um eine Translation oder eine Rotation handelt, werden die Antriebe in zwei Hauptkategorien eingeteilt, nämlich Linear- und Rotationsantriebe.
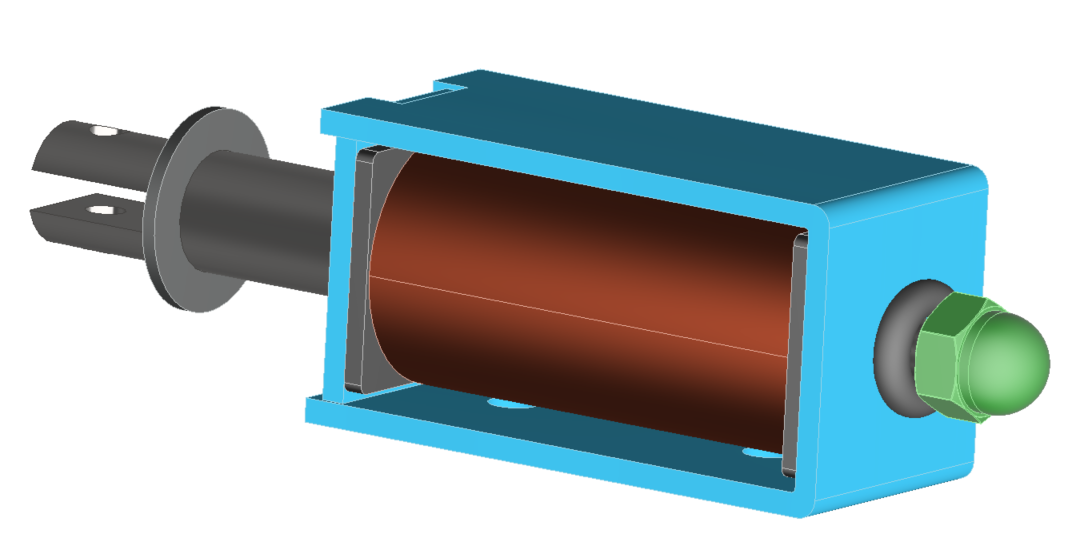
Lineare elektromagnetische Aktuatoren mit Solenoidtyp sind in industriellen Anwendungen weit verbreitet. Sie sind Teil verschiedener elektromagnetischer Geräte, die auf unterschiedlichen Steuerungsmechanismen basieren.
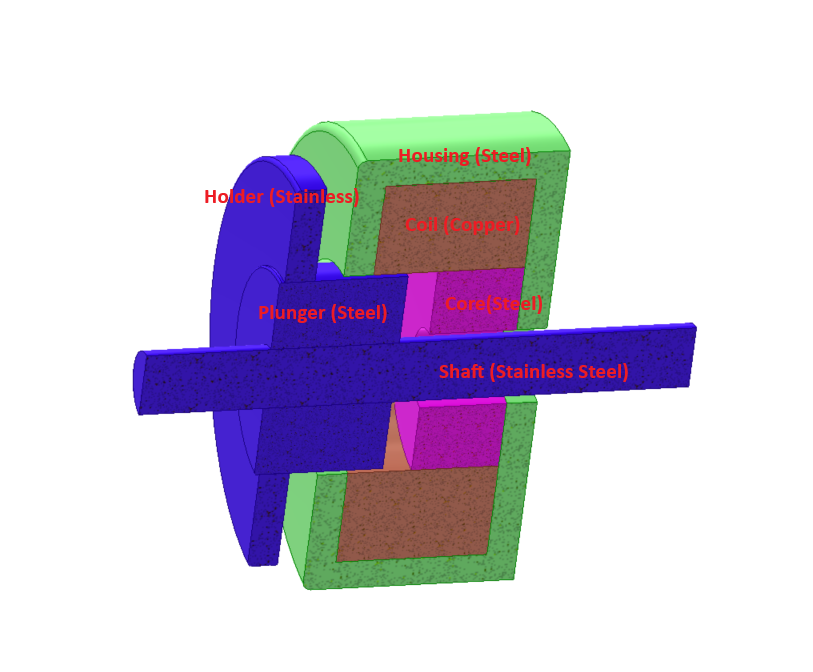
Elektromagnetische Aktuatoren sind elektromechanische Komponenten, mit denen elektrische Energie in eine mechanische Bewegung umgewandelt wird. Sie decken translatorische und rotatorische Bewegungen ab. Gleichstromaktoren bestehen im Allgemeinen aus Permanentmagneten, Magnetspulen und ferromagnetischen Teilen.
Magnetische Aktuatoren basieren auf einem elektromagnetischen Feld, um elektrische Energie in mechanische Energie umzuwandeln. Abhängig von der Art der erzeugten Bewegung; Bei elektromagnetischen Antrieben mit linearer oder rotatorischer Bewegung werden zwei Kategorien unterschieden: rotatorischer und linearer Antrieb.
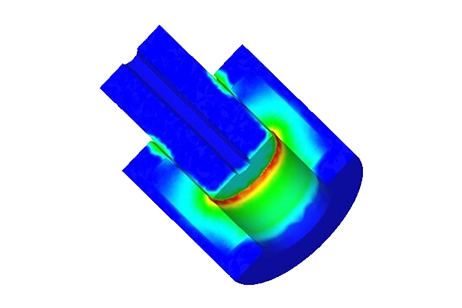
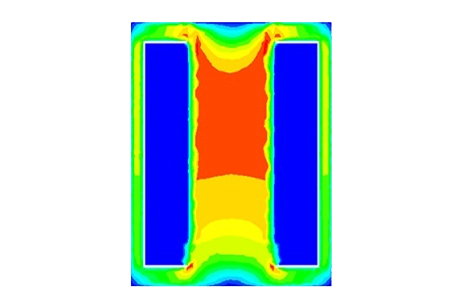
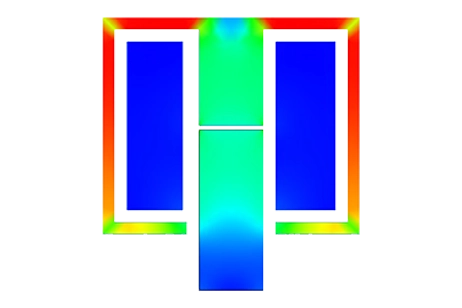
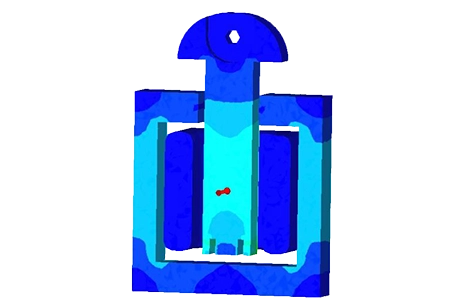
Es wurde eine 3D-FEM-Simulation eines T-förmigen elektromagnetischen Aktuators durchgeführt, und die Ergebnisse werden in diesem Artikel erläutert
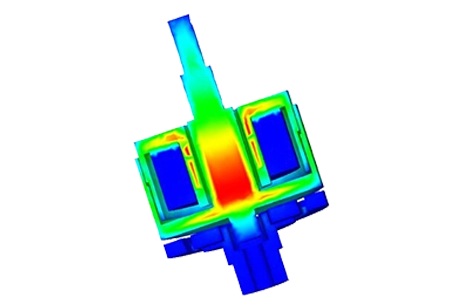
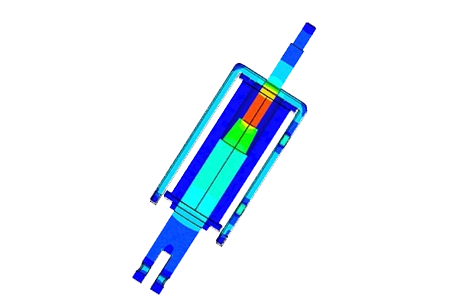
A voice coil actuator based on the Lorentz force is analysed with 2D/3D finite element simulations to compute magnetic flux density, Lorentz force, inductance, back EMF, current response and mechanical output (displacement, speed, acceleration) under different DC voltage and current excitations. An electrothermal model evaluates winding losses and temperature rise, and all key quantities such as force and back EMF sensitivity are compared against published experimental data, including a brief comparison with solenoid actuator behaviour.
This note analyses a voice coil actuator with 3D finite element simulations, focusing on transient current and force response under different DC voltages and on electrothermal behaviour due to copper losses in the winding. The study reports current rise times, steady-state force at a fixed stroke, winding loss for 20 V and 200 V cases, and the resulting temperature distribution and evolution, highlighting the actuator’s electrical, mechanical and thermal limits.
This application note analyses a voice coil actuator with 3D finite element simulations, combining a static study and an electromechanical study. The static analysis computes magnetic flux, Lorentz force versus stroke and current, force sensitivity, inductance variation and back-EMF constant, with results compared to reference measurements. The electromechanical analysis evaluates coil position, speed and acceleration for different DC voltages, linking electrical excitation to dynamic response and confirming the actuator’s linear force–current behaviour and nearly constant inductance over the useful stroke.
Coupled electromagnetic–thermal FEM is used to predict coil losses, temperature rise, and design trade-offs in a DC linear actuator.