EMAG: Elektromagnetische Simulation für niedrige bis mittlere Frequenzen | EMWorks
EMAG ist ein spezialisiertes Modul innerhalb von EMWORKS, das sich auf die Simulation elektromagnetischer Felder im Nieder- bis Mittelfrequenzbereich konzentriert. Entwickelt für Ingenieure und Forscher, bietet EMAG fortschrittliche Werkzeuge zur Analyse, Optimierung und Simulation elektromagnetischer Phänomene in verschiedenen Anwendungen wie elektrischen Maschinen, Aktuatoren, Sensoren, Transformatoren und mehr. Seine Vielseitigkeit und Präzision machen es zu einem unverzichtbaren Werkzeug für Branchen wie Automobilindustrie, Luft- und Raumfahrt, Medizintechnik und Energietechnik.
.webp)
EMAG – Überblick
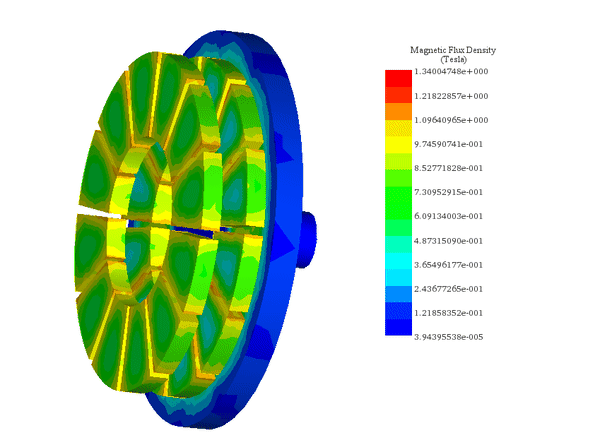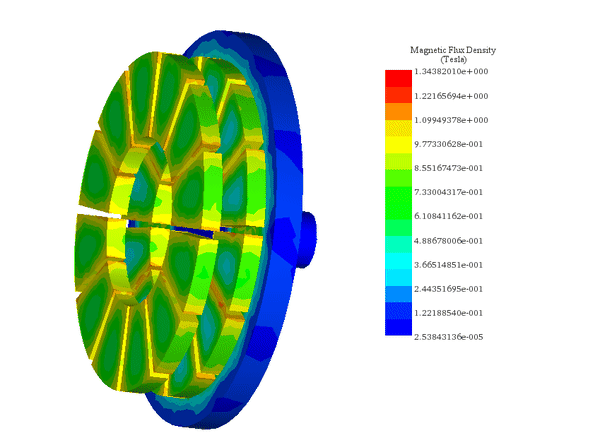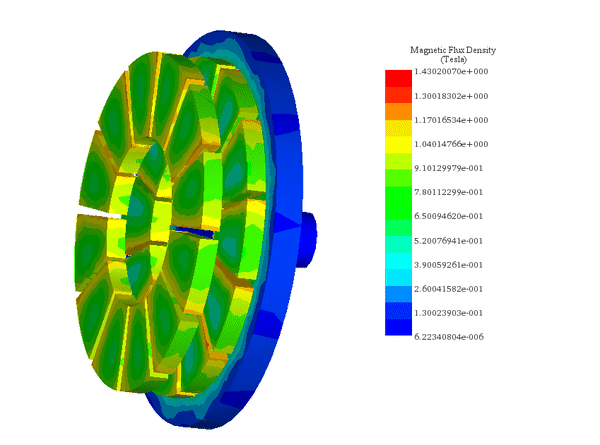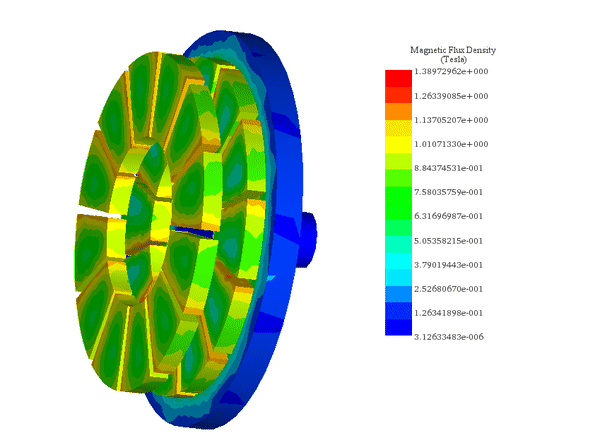
EMAG führt elektromagnetische Feldanalysen im Nieder- bis Mittelfrequenzbereich an 2D- und 3D-Modellen wie Motoren, Aktuatoren, Transformatoren und Sensoren durch. Das Modul unterstützt Spulen, Permanentmagnete, Leiter und ferromagnetische Bauteile in vollständigen 3D- oder 2D-/achsensymmetrischen Konfigurationen, mit optionalen parametrischen Sweeps sowie thermischer oder struktureller Kopplung. Die Ergebnisse umfassen Feldverteilungen, magnetische Flussdichte, Stromdichte, Verluste, Kräfte und Drehmomente über die gesamte Geometrie hinweg und ermöglichen einen direkten Vergleich verschiedener Designoptionen.
EMAG Analyseoptionen

Magnetostatische Analyse
Berechnet DC-Magnetfelder, magnetische Kräfte, Flusspfade und Sättigungsgrade.
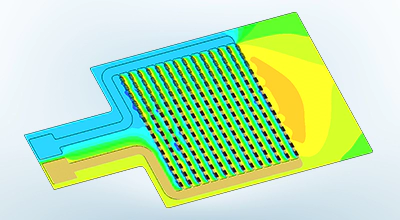
Leitungsanalyse
Bewertet den stationären Stromfluss und das ohmsche Verhalten in leitfähigen Materialien.
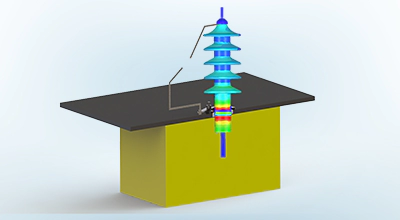
Elektrostatische Analyse
Berechnet die Verteilung des elektrischen Feldes unter statischen Spannungs- und Ladungsbedingungen.
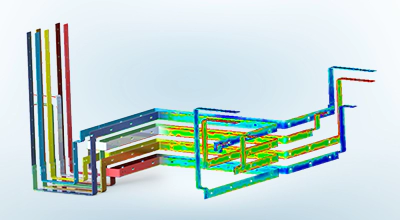
AC-Magnetische Analyse
Löst sinusförmige magnetische Felder sowie frequenzabhängige elektromagnetische Effekte.
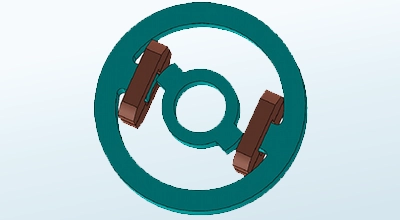
Transiente Magnetische Analyse
Analysiert zeitlich veränderliche Magnetfelder, die durch Schaltvorgänge oder gepulste Anregungen erzeugt werden.
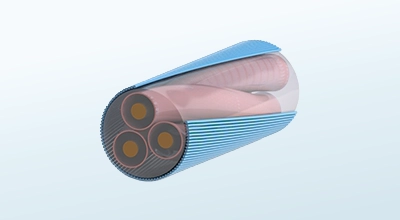
Wechselstrom-Elektrik
Modelliert zeitlich wechselnde elektrische Felder in leitfähigen und dielektrischen Medien.
Fordern Sie jetzt Ihre kostenlose EMAG-Testversion an!
Erfahren Sie, wie EMAG Ihre Konstruktionsentwürfe transformieren und Ihren Produktentwicklungsprozess optimieren kann.
Multiphysikalische Kopplung
EMAG koppelt die elektromagnetische Analyse mit Bewegungs-, Struktur- und Thermosolvern für Geräte, bei denen elektromagnetische Felder mit mechanischen Effekten und thermischen Einflüssen interagieren.

Bewegungskopplung
Koppelt elektromagnetische Felder mit mechanischer Bewegung, um Kraft und Drehmoment in Abhängigkeit von Position oder Zeit in Motoren, Aktuatoren, Solenoiden, Relais und magnetischen Systemen zu berechnen.
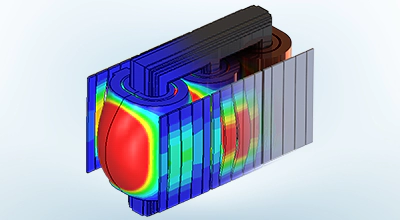
Strukturelle Kopplung
Abbildung elektromagnetischer Kräfte und Verluste auf strukturelle und thermo-mechanische Analysen zur Bewertung von Verschiebung, Spannung, Dehnung und Sicherheitsfaktoren.

Wärmekopplung
Verknüpft elektromagnetische Verluste mit stationärer oder transienter thermischer Analyse zur Berechnung von Temperatur, Temperaturgradienten und Wärmestrom, optional unter Berücksichtigung temperaturabhängiger EM-Eigenschaften.
.gif)
Schaltungskopplung
Die Schaltungskopplung in EMWORKS integriert das 3D-elektromagnetische Modell mit einem elektrischen Schaltplan. Diese Zweiweg-Interaktion ermöglicht eine realitätsnahe Simulation von Geräten wie Motoren und Transformatoren im transienten und stationären Betrieb und erfasst Effekte wie Gegen-EMK (Back-EMF) und magnetische Sättigung.
EMAG Anwendungen
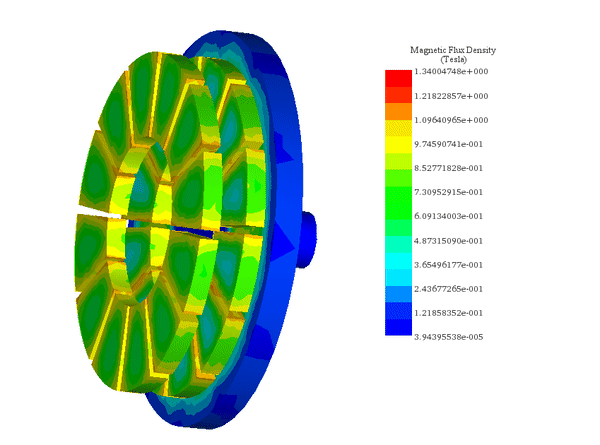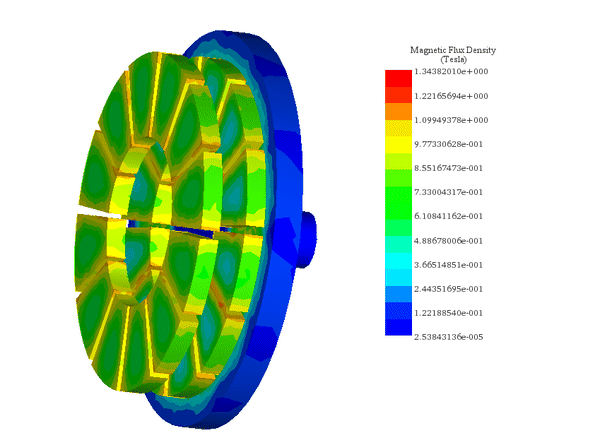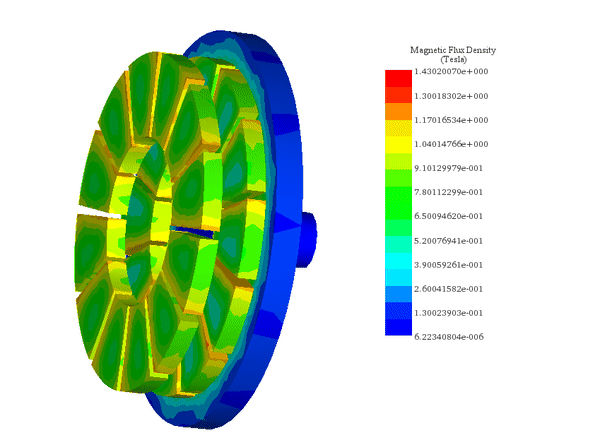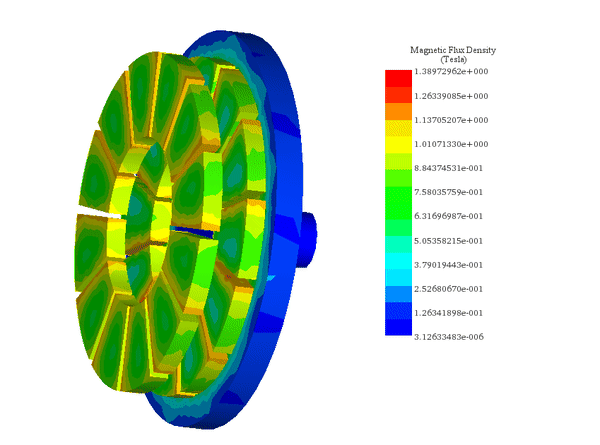
Motors and Generators
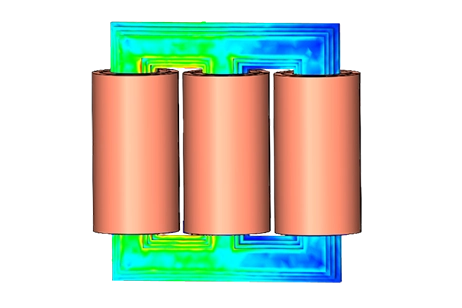
Transformers and Inductors
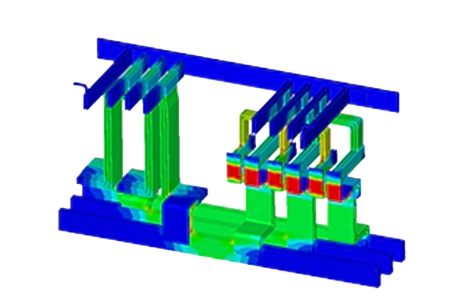
Busbars and Power Distribution
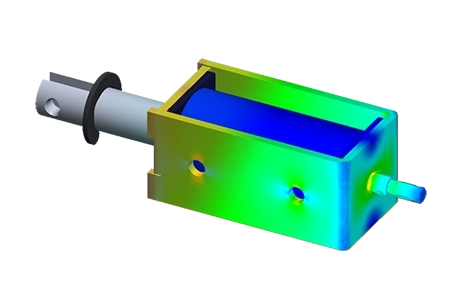
Actuators and Solenoids
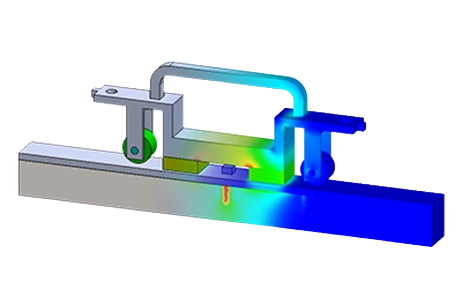
Eddy-Current NDT