| |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Thursday, September 08, 2022
Session 1: 03:00 PM CEST, 01:00 PM GMT
Session 2: 02:00 PM EDT, 06:00 PM GMT
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Thursday, September 15, 2022
Session 1: 03:00 PM CEST, 01:00 PM GMT
Session 2: 02:00 PM EDT, 06:00 PM GMT
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Thursday, September 22, 2022
Session 1: 03:00 PM CEST, 01:00 PM GMT
Session 2: 02:00 PM EDT, 06:00 PM GMT
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Sunday, October 9, 2022 - Thursday, October 13, 2022
Detroit, Michigan USA
Booth #321
|
|
|
| |
| |
 |
|
|
|
Monday, October 31, 2022 - Thursday, November 3, 2022
Nashville, Tennessee, USA
Booth #319
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Application Note |
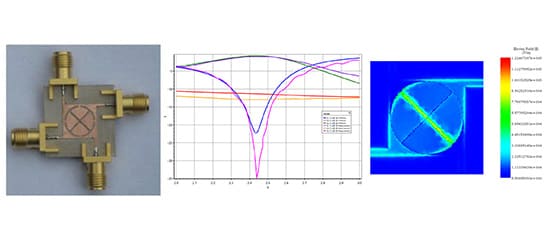
| Design and Simulation of a Compact Planar Micro-Strip Crossover for Beam Forming Networks Using Hfworks for SOLIDWORKS |
Crossovers are very interesting passive devices in monolithic Integrated Circuits (IC) and antenna arrays. These devices maintain signal purity when transmission lines intersect. There are several types of crossovers. Printed planar crossovers are the most used thanks to their compact and simple structure.
In this article, a compact planar crossover is designed using the CAD SOLIDWORKS and simulated using the full wave 3D simulator HFWorks. An S Parameter analysis is conducted to investigate the electromagnetic behavior of this structure. Figure 1 shows the fabricated prototype of the proposed crossover.
Read More >
|
 |
|
|
| |
| Blog Post |
| Design and Analysis of Wireless Power Transfer Charger for Electric Vehicles |
| In simple terms, wireless power transfer is the transmission of electric power without any direct physical wire or cable connections. The power transfer is usually based on the technology that utilizes electric, magnetic, or electromagnetic fields. WPT happens by creating an alternating magnetic field on the transmitter coil. This magnetic flux is then converted into an electrical current in the receiver coil.? The generated electrical current depends on the amount of flux generated by the transmitter coil, and how much of a percentage the receiver coil can capture. The distance, size, and position of the receiver coil relative to the transmitter coil decide the “coupling factor or coupling coefficient” of the two coils.
Read More >
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
EMWorks Inc.
150 Montreal-Toronto Blvd, Suite 120,
Montreal, Quebec, H8S 4L8, Canada.
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|