What is EM simulation?
Electromagnetic (EM) simulation uses computational methods to analyze electric and magnetic fields in electrical devices, providing crucial insights into design performance. This process allows engineers to access essential parameters like inductance, impedance, and capacitance, crucial for designing motors, generators, transformers, and more. By leveraging EM simulation, designers can bypass the costly and time-consuming process of prototype testing, enabling faster optimization and improvement of their products.
Benefits of EM simulation
EM simulation has become a crucial part of the design process, enabling the creation of optimized, competitive products across global markets. Its integration into product development accelerates the transition from concept to reality, particularly through 3D CAD software like Autodesk Inventor. Tools like EMS for Autodesk Inventor streamline design validation and optimization, eliminating the need for physical prototypes. When combined with mechanical and thermal simulations, EM simulation offers a comprehensive understanding of a device's performance. The use of 3D printing to materialize designs for pre-manufacturing tests further revolutionizes the electrical devices industry, showcasing a modern, efficient digital engineering workflow.

Figure 1 - The product development workflow inside Autodesk Inventor
Benefits of integration inside Autodesk Inventor
Autodesk Inventor, popular among engineers for designing electrical machines and devices, integrates seamlessly with EMS for enhanced EM simulation capabilities. This integration allows for:
Direct CAD Simulation: Use of 3D models for simulation within Inventor, maintaining design integrity.
Efficient Design Revisions: Simulation insights enable substantial design modifications without leaving the Inventor platform.
Ease of Use: The familiar Inventor interface simplifies the learning process for conducting EM simulations.
This streamlined approach accelerates and simplifies the process of simulation-based product development, enhancing design optimization.
Application areas
EM simulation spans a wide array of application areas, from compact electrical machines to sizable transformers, accommodating various types of excitation such as DC and AC. The scope of electromagnetics is so broad that any attempt to categorize its applications might not fully capture its extensive reach. Acknowledging this, it's important to note the overlap among the diverse applications and devices within the field. Key areas include:
- Rotary and Linear Actuators, Motors, and Generators: Essential for motion and power generation.
- Transformers and Inductors: Critical for power conversion and electrical energy distribution.
- Insulators, High Power Switches, Bus Bar Networks, Induction Heaters: Vital for energy transfer, heating processes, and electrical safety.
- Sensors, Motion Controllers, and Measurement Devices: Fundamental for automation, precision control, and data acquisition.
- Permanent Magnet-Based Devices, Magnet Arrays, Magnetic Levitation: Innovative applications in transportation, material handling, and beyond.
These examples underscore the vast, interwoven landscape of EM simulation applications, highlighting its critical role in advancing technology across multiple domains.
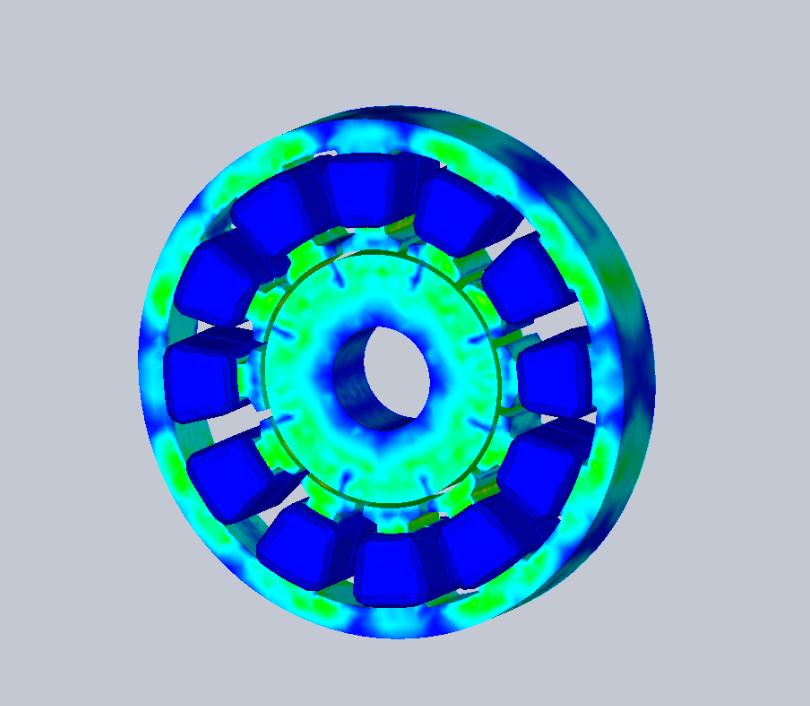
Figure 2 - EMS for Inventor can calculate the magnetic field inside a motor and also the cogging torque
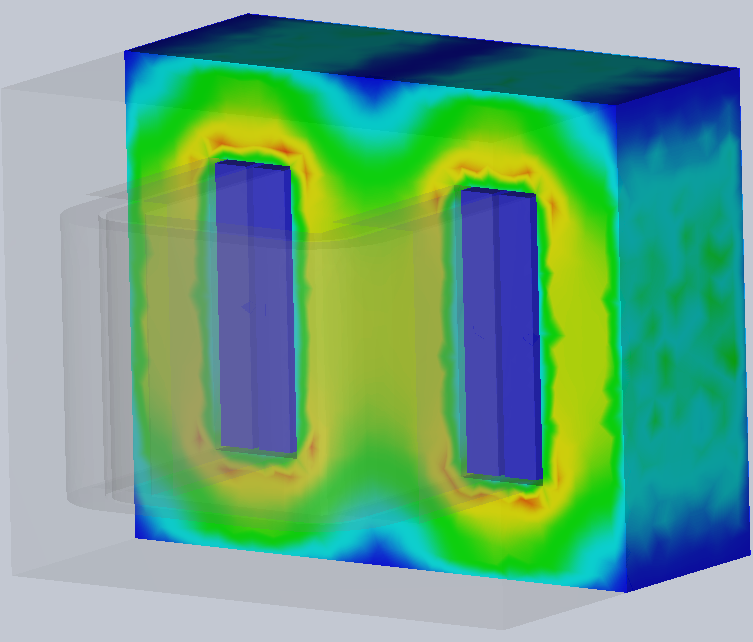
Figure 3 - EMS for Inventor can help visualize the losses in the core of a transformer
Conclusion
Integrating EM simulation with Autodesk Inventor stands as a cornerstone in advancing the design and optimization of electrical devices. This fusion enables engineers to leverage the comprehensive capabilities of EM simulation directly within a familiar CAD environment, significantly accelerating the development cycle from conceptualization to final product. Highlighted in the application note, this synergy not only streamlines the process of validating and refining designs but also greatly reduces the reliance on physical prototypes. As a result, Autodesk Inventor with EM simulation becomes an invaluable asset for engineers aiming to achieve efficiency, precision, and innovation in electrical device development.